Antibody screening test
Practically all people living with HIV and/or HCV have antibodies to the respective viruses. Antibodies usually develop during the first month of infection but it can take a longer time before tests can detect them.
Practically all people living with HIV and/or HCV have antibodies to the respective viruses. Antibodies usually develop during the first month of infection, but it can take a longer time before tests can detect them. The time after infection and before antibodies can be detected is called ‘the window period’ and it can be as long as 3 months for HIV and up to 6 months for HCV. Antibody tests for HIV and HCV may show false negative results for HIV and HCV antibodies during this time period. During the window period an infected person can pass the virus on to others.
WINDOW PERIOD
- Time from initial infection until antibodies are detected
- It is usually 3-8 weeks before antibodies are detected
- Up to 3 months for HIV and up 6 months for HCV
- Test may show false-negative for antibodies during this time period
- People can still pass the virus to others during this period
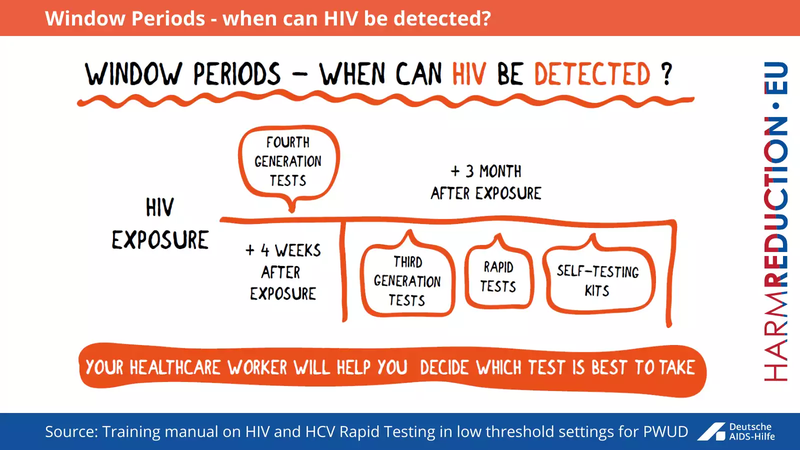
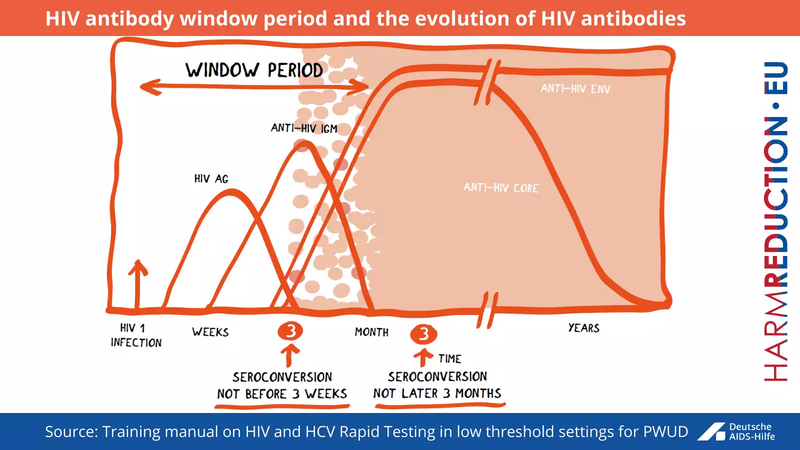
The window period is a stage when a person has been infected with HIV or HCV, but body hasn’t yet created antibodies. “Seroconversion” is the term used to describe the change when there are enough of antibodies to produce a positive antibody test. In other words, blood is negative to HIV or HCV antibody tests during a short time period after infection, but converts to positive for antibodies after a certain period, generally, 3-8 weeks after the initial infection and not later than 3 months for HIV (Fig 8). If the HIV antibody test result is negative within three months from the exposure to the virus the test should be repeated once 3 months have passed from the time. In the case of HCV, the test should repeated once 6 months have been passed since the time of exposure to the virus.
Testing in the Window Period
Polymerase chain reaction
The fist marker for HIV infection that can be detected is the presence of HIV-RNA which can be found as early as 11 days after transmission. Even though polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests can be used as an additional test for helping to detect HIV-infections during the window period, there are several reasons why a PCR test is not suitable alone for primary diagnostics. It is expensive, labor intensive and it needs special facilities. In addition, because of its sensitivity and specificity, all preliminary positive PCR results must be confirmed with HIV-antibody tests to confirm infection. PCR tests are mainly used to monitor the progression of infection and treatment outcomes. In addition, it is used in the diagnosis of HIV infection in infants born to mothers living with HIV.
Antibody / p24 Antigen combo assay
These assays detect both HIV antibodies and antigens. The mean time between HIV-infection to the possibility of detecting the HIV p24 antigen is 16 days. Because the HIV p24 antigen can be detected in plasma in only approximately 50% of HIV-infected individuals, these tests cannot be used alone for primary diagnostics. As in the case of PCR, all preliminary p24 antigen positive results must be confirmed with HIV-antibody test to confirm the infection.
- Prev: HIV, HCV, TB - additional res…
- 2.1 (current)
- Next: Rapid Test


