HCV transmission
1.
Basic information about HIV, HCV…
1.1
2.
Different types of tests
2.1
3.
Pre- and post-test counselling
3.1
4.
Developing services and attracti…
4.1
5.
Gender-specific approach to serv…
5.1
6.
Linkage to care
6.1
7.
Improving quality
7.1
8.
HIV/HCV community-based counsell…
8.1
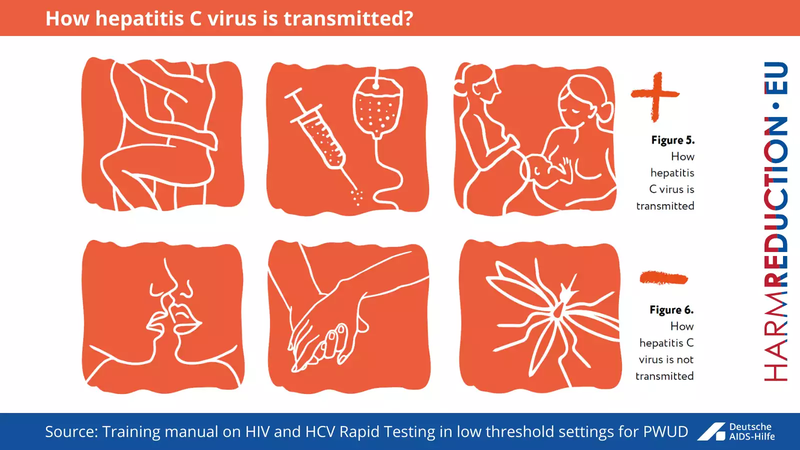
The hepatitis C virus is a blood-borne virus. It is most commonly transmitted through exposure to small quantities of blood.
The hepatitis C virus is a blood-borne virus. It is most commonly transmitted through exposure to small quantities of blood through:
- the sharing of injection equipment by people who inject drugs;
- the reuse or inadequate sterilization of medical equipment, especially syringes and needles in health care settings;
- the transfusion of unscreened blood and blood products;
- tattooing and piercing with inadequately sterilized equipment;
- household risks when living with persons with HCV – sharing razors, tooth brushes, nail clippers other things coming in contact with blood.
HCV can also be transmitted sexually and can be passed from a mother who is living with the virus to her baby however, these modes of transmission are much less common (Fig 5).
HCV is not transmitted by air or water, mosquitoes, ticks or other insects, saliva, tears, or sweet that is not mixed with blood of an HCV infected person or by shaking hands, hugging, sharing drinking glasses and kissing (Fig 6).
Published: 2022


